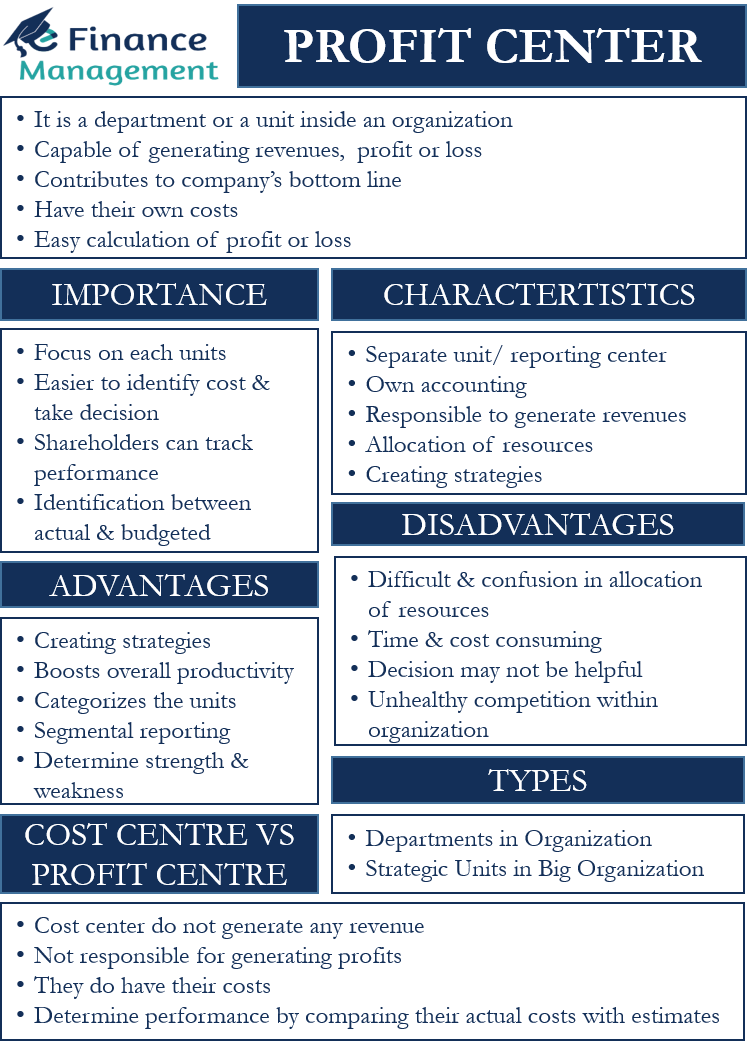
Profit Center: Characteristics vs a Cost Center, With Examples

In effect, that person has responsibility for all financial aspects of the investment centre. The principal object of a profit centre is to generate and maximise the profit by minimising the cost incurred and increasing sales. However, this division is still not appropriate because the departments are big. Therefore, we can make a comparison of the cost that is accumulated cost centre-wise, with the standards, estimates and budgets.
Cost compared to budget:
KPIs for profit centers include measures like sales growth, gross profit margin, return on investment (ROI), and contribution margin. Performance evaluations assist in identifying successful profit centers and addressing underperforming ones through strategic adjustments. Cost centers are typically responsible for managing costs, while profit centers are responsible for generating revenue. Therefore, a profit center may be better if the organization wants to hold managers accountable for revenue generation. Understanding the distinction between profit centers and cost centers is crucial for effective organizational management.
Give a few examples of cost centres.
He then said that there are only cost centers in a business and no profit center. If any profit center existed for a business, that would be a customer’s check that hadn’t been bounced. The concept of a profit center is a framework to facilitate optimal resource allocation and profitability. To optimize profits, management may decide to allocate more resources to highly profitable areas while reducing allocations to less profitable or loss-inducing units.
What is a Cost Center?
These costs are generally monitored by analysing and deducting the actual cost incurred with the standard cost. A cost centre is a department or a unit that supervises, allocates, segregates, and eliminates all sorts of costs related to a company. The cost centre’s prime work is to check the cost of an organisation and to limit the unwanted expenditure that the company may acquire. Invest in employee training to ensure staff members have the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their jobs effectively. It can include training in process improvement, financial analysis, and budgeting. Implement cost-saving measures to ensure that the cost center operates efficiently.
These two types of business units play fundamentally different roles within a company, each contributing uniquely to overall performance and strategic goals. Unlike a cost center, a profit center is a distinct organizational unit that is responsible for generating revenue and directly contributing to the profitability of the organization. Profit centers are typically found in organizations where different products, services, or business lines are managed separately, each with its own revenue and cost structure. Evaluating the financial performance of profit centers requires a nuanced approach that goes beyond simple revenue figures. One of the most insightful metrics is the profit margin, which measures the percentage of revenue that remains as profit after all expenses are deducted.
Accounting Business and Society
- Hence, the subdivision of the factory into a number of departments becomes essential.
- As an example, they may investigate the customer financing arm of the business to see if it is creating the necessary profit.
- This autonomy allows profit centers to make decisions that directly affect their financial performance, such as pricing strategies, marketing efforts, and product development.
- In conclusion, the seamless coordination and operation of Profit Centers and Cost Centers ensure that business run smoothly and at scale.
- When the actual quantity is more than the standard quantity, the variance would be unfavorable and vice-versa.
- The achievement of a profit centre is examined by subtracting the actual cost from the budgeted cost.
For instance, a well-managed human resources department can improve employee satisfaction and retention, leading to a more motivated and efficient workforce. Cost centers are evaluated based on their ability to control costs, optimize resource utilization, and achieve budgeted targets. Key performance indicators (KPIs) for cost centers include measures like cost variances, cost per unit of output, and cost reduction initiatives. Regular performance evaluations help identify areas of improvement and drive operational efficiency.
For instance, a customer service department might use data analytics to track response times and customer satisfaction, allowing them to refine their processes and enhance service quality. This focus on continuous principles of sound tax policy improvement not only reduces costs but also enhances the overall effectiveness of the organization. Profit centers serve as the driving force behind a company’s revenue generation and financial growth.
Profit centers are crucial to determining which units are the most and the least profitable within an organization. They function by differentiating between certain revenue-generating activities. This facilitates a more accurate analysis and cross-comparison among divisions. A profit center analysis determines the future allocation of available resources and whether certain activities should be cut entirely. As an example, they may investigate the customer financing arm of the business to see if it is creating the necessary profit. Cash flow analysis is also essential for evaluating the financial performance of profit centers.
No Comments